Since their launch, public cloud environments have been different in the way companies that use them to approach IT security.
The major public cloud providers (e.g. AWS, Azure, Google, IBM) implement and present to their customers the shared responsibility model concerning IT security for the service used. Shared responsibility model represents a Security framework in which Cloud Service Providers define the responsibilities of each entity (CSP and Customer) in different services offered (e.g. IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, etc.). It dictates the security obligations of the cloud computing provider and its users to ensure responsibility and accountability. We will refer in this current blog article specifically to IaaS services.
When it comes to Microsoft, we cite from the conclusions in the document – “Shared Responsibilities for Cloud Computing “. “For IaaS solutions, the elements such as buildings, servers, networking hardware, and the hypervisor should be managed by the platform vendor. The customer is responsible or has a shared responsibility for securing and managing the operating system, network configuration, applications, identity, clients, and data.”
On AWS web page: “Customers that deploy an Amazon EC2 instance are responsible for management of the guest operating system (including updates and security patches), any application software or utilities installed by the customer on the instances, and the configuration of the AWS-provided firewall (called a security group) on each instance. For abstracted services, such as Amazon S3 and Amazon DynamoDB, AWS operates the infrastructure layer, the operating system, and platforms, and customers access the endpoints to store and retrieve data. Customers are responsible for managing their data (including encryption options), classifying their assets, and using IAM tools to apply the appropriate permissions.”
Graphically and simplified, the shared responsibility model can be represented as in the bellow picture.
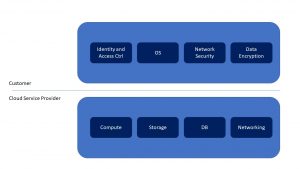
Data is moving from traditional on-prem, where IT implemented security protections, to data centers that are outside their control. Classic on-prem security cannot defend data in the Cloud, leaving it at risk. The threats targeting classic infrastructure are now targeting the companies’ data in the cloud. In fact, with new malware in the cloud, once a VM is infected, it can then easily propagate to other VMs. Sometimes to corporate on-premises infrastructure using the VPN link between on-prem and cloud.
Shared, multi-tenant infrastructure to support millions of customers all over the world are the way public cloud is built and architected. Although all public cloud providers have as foundation enhanced security, the public cloud provider security controls will have no knowledge of specific customer traffic. Thus, it is unable to determine between normal and malicious content. This represents the biggest problem to DevOps and IT security departments. They have to provide the same level of security to company data in the cloud as if it were hosted on-premises.
In order for enterprises to completely move their infrastructure to the cloud, they need to understand where each party responsibility and accountability lies and the difference between protecting the cloud infrastructure and the data that resides in the cloud. IaaS providers refer to this as the shared responsibility model.
Understanding the roles and responsibilities of each entity (customer and cloud providers) helps organizations make the best decisions concerning the security of their cloud environments. It also ensures that an organizations cybersecurity strategy efficiently and cost-effectively aligns with the rest of the business goals while delivering consistent protections for all corporate data both on-premises and in the cloud.
In addition to the security offered by the IaaS provider, we believe that enterprises must deploy their own Cloud Security Solutions. We think that Check Point CloudGuard is the best solution on the market today for securing your Public Cloud.
Check Point CloudGuard compliments native cloud service provider (CSP) security controls to ensure public IaaS customers can fulfill their shared security responsibilities. With Check Point CloudGuard, customers can secure their workloads and applications running in hybrid and public cloud infrastructures, minimizing threats from breaches, data leakage as well as zero-day threats. Whether your cloud strategy centers around public or hybrid IaaS, VPN replacement, multi-cloud routing, or cloud DMZ, Check Point CloudGuard helps secure all your cloud assets while fully supporting the elastic, dynamic and cost-effective nature of the cloud.
Roca Networks can help you deploy the best Cloud Security, based on Check Point Software Technologies solutions, whether on AWS, Azure, Google or even Private Cloud built on VMware or OpenStack. We have strong experience and know-how in both Cybersecurity and in Cloud-Computing. We have helped Customers deploy Security Solutions on-premises and in Public Cloud Infrastructures. If you need assistance in securing your infrastructure in public cloud environments- contact us at info@rocanetworks.com or leave your data in our contact form – https://www.rocanetworks.com/contact-us and you will be able to take advantage of our experience and certified knowledge.


